Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men worldwide. However, the good news is that when detected early, it is one of the most treatable.
This article breaks down everything you need to know about prostate health, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and how your diet and lifestyle can make a difference.
What Is the Prostate?
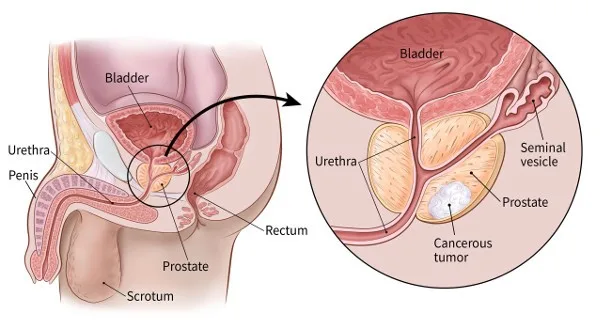
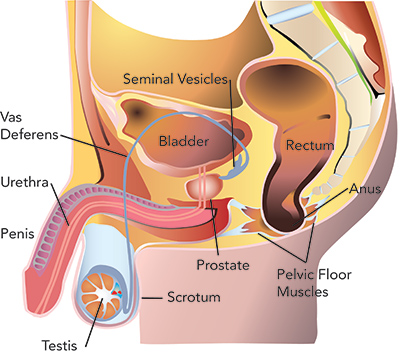
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland found just below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. Its primary function is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation. Though small, the prostate plays a major role in reproduction and urinary function.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate begin to grow abnormally and uncontrollably. In some cases, the cancer remains confined to the prostate. In others, it can spread (metastasize) to nearby tissues like lymph nodes, bones, or even the lungs.
There are two main types:
- Slow-Growing Prostate Cancer
Progresses very slowly and may not require immediate treatment. - Aggressive Prostate Cancer
Grows rapidly and can spread quickly; it requires urgent medical intervention.
Who Is at Risk?
Some men are more likely to develop prostate cancer due to the following risk factors:
- Age: Risk increases significantly after age 50. Most cases are diagnosed after 65.
- Family History: Having a father, brother, or close relative with prostate cancer raises your risk.
- Race: African men are at higher risk, especially for aggressive forms.
- Lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake contribute to risk.
- Genetic Mutations: Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are linked to increased prostate cancer risk.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
In its early stages, prostate cancer may not cause any symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Blood Test: Elevated levels may signal a problem.
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): A physical check of the prostate by a doctor.
- Biopsy: If cancer is suspected, a sample of prostate tissue is taken and examined.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans may be done to assess if cancer has spread.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and type of prostate cancer:
- Active Surveillance: For slow-growing cases, monitoring may be all that’s needed.
- Surgery: Removal of the prostate (prostatectomy) may be performed for localized cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Used alone or with other treatments to kill cancer cells.
- Hormonal Therapy, Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy: For advanced or metastatic cancer.
All treatments have potential side effects, so decisions should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented?
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, the following steps can reduce your risk:
- Healthy Diet: Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods and red meat.
- Regular Exercise: Supports weight management and overall health.
- Routine Screening: Men over 50 should talk to their doctor about screening. Those at higher risk may need to start earlier.
- Lifestyle Choices: Quit smoking and reduce alcohol intake.
Top Natural Foods for Prostate Health
Certain foods may support prostate health and lower your risk:
- Tomatoes (rich in lycopene)
- Soursop
- Beans
- Carrots
- Cabbage
- Onions (blend 2 bulbs, take half a glass morning and night for 1 week)
- Walnuts
Take Charge of Your Health
Your health starts in your kitchen. Junk foods may taste good, but they do your body no favors in the long run.
- Eat right
- Exercise often
- Get screened
- Make informed choices